What is weight loss?
Achieving weight loss is a primary objective for many individuals across the US who aim to enhance their overall health and well-being. This process entails deliberately reducing excess body fat by adopting a thoughtful blend of nutritional modifications, increased exercise, and significant lifestyle changes. More than just appearance, maintaining a healthy weight plays a crucial role in preventing and managing various obesity-related health issues, leading to a better quality of life.
These treatments have been developed to aid in your efforts to improve your weight management for the long term. With GLP-1's trailblazing the market into the future. With proven results worldwide, they are a viable option for anyone seeking to improve their livelihood.
Take your first steps with Médetone LLC today.
Browse the collection
Explore our range of weight loss solutions.
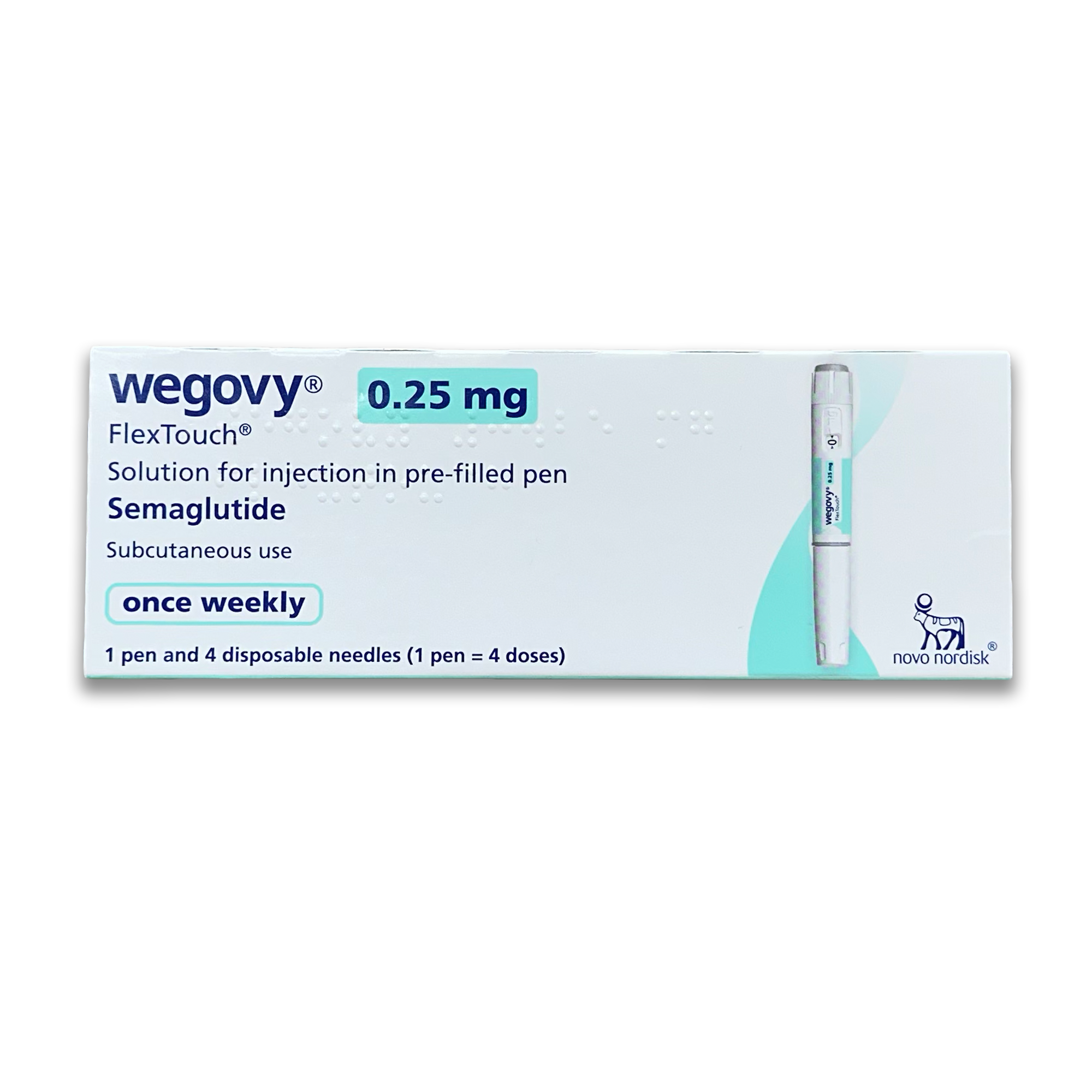
Wegovy (Semaglutide) Injections
Start your Consultation
Start your consultation on the condition page to check your eligibility.
The Consultation Process

How does the online consultation work?
To begin, you’ll fill out a secure online questionnaire designed to gather important details about your health and weight loss objectives. This information enables our licensed healthcare providers to evaluate your suitability for treatment. After submitting the questionnaire, your answers will be thoroughly reviewed, and if necessary, a clinician may reach out to you for further clarification. Once approved, a prescription will be issued, and your treatment will be dispatched from our pharmacy located on the East Coast.

Will I need to schedule an appointment, or will someone contact me directly?
No appointment is required. The consultation is fully flexible and can be completed at any time that works best for you. You have the option to pause the questionnaire and return to it whenever you wish. Once submitted, one of our healthcare professionals will review your information within 24 hours. If you don’t hear back within that period, please reach out to us at info@medetone.com, and we’ll get back to you promptly.

What is the cost of the online consultation?
The online consultation is entirely free of charge. Payment is only required if you qualify for treatment. If you are deemed ineligible, any payment made will be fully refunded. Additionally, you can have a preliminary, no-obligation conversation with a clinician to help identify the most suitable weight loss option for you.
What are the key differences between Mounjaro & Wegovy?
What is Mounjaro?
The newest FDA-approved treatment for weight management and type 2 diabetes.
Includes tirzepatide, a medication that acts on two important hormones: GLP-1 and GIP.
This dual-action approach helps suppress appetite while also supporting better blood sugar regulation.
Intended to deliver improved results when used alongside lifestyle modifications.
What is Wegovy?
Approved for weight management in adults who are overweight or obese.
Contains semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist medication.
Works by mimicking a natural hormone that influences the brain’s appetite regulation centers.
Supports reduced hunger and calorie consumption to encourage long-term weight loss.
Are there treatment options available if I prefer not to use injectable medications?
How do the chemical compositions of oral treatments differ from those of injectable medications?
Although oral and injectable weight loss medications can contain the same active ingredient (like semaglutide), their chemical formulations are specifically tailored to their method of delivery. Injectable medications are administered directly into the bloodstream, while oral medications must withstand the digestive process, resulting in different designs to maintain their effectiveness.
Key distinctions include:
- Injectables bypass the digestive tract, allowing for more efficient absorption; oral medications often require absorption enhancers.
- Oral tablets are formulated with protective coatings and carriers to withstand stomach acid.
- Injectables are often chemically more stable, especially for peptide-based drugs.
- Injectables generally allow for higher drug levels in the blood.
- Oral tablets contain more excipients (binders, coatings, etc.) than injectables.
Do oral medications offer the same effectiveness as injectable treatments?
Oral weight loss medications can be effective, but they don’t always function identically to injectable treatments. Even when containing the same active ingredient, oral medications are absorbed differently, which can slightly impact how much of the drug is available to work in the body.
That said, for many individuals, oral options offer a convenient and clinically effective alternative.
Key points:
- Oral medications may deliver lower drug levels into the bloodstream compared to injectables.
- Higher oral doses are often used to make up for reduced absorption.
- Clinical trials show that oral semaglutide (like Rybelsus) can produce weight loss comparable to injections in some individuals.
- For those who prefer to avoid injections, oral treatments provide an effective option when taken as directed and consistently.